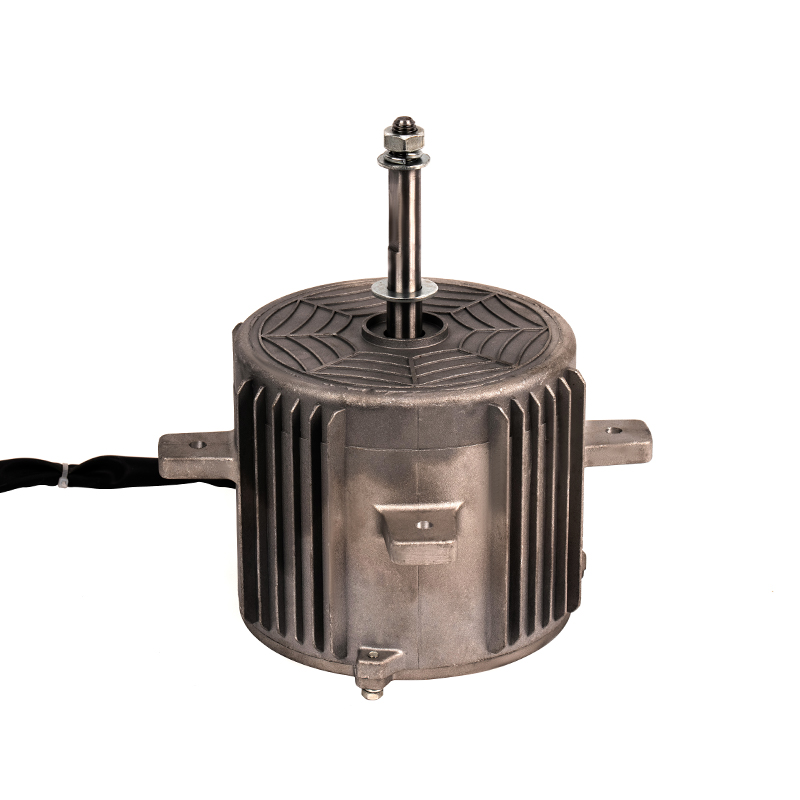
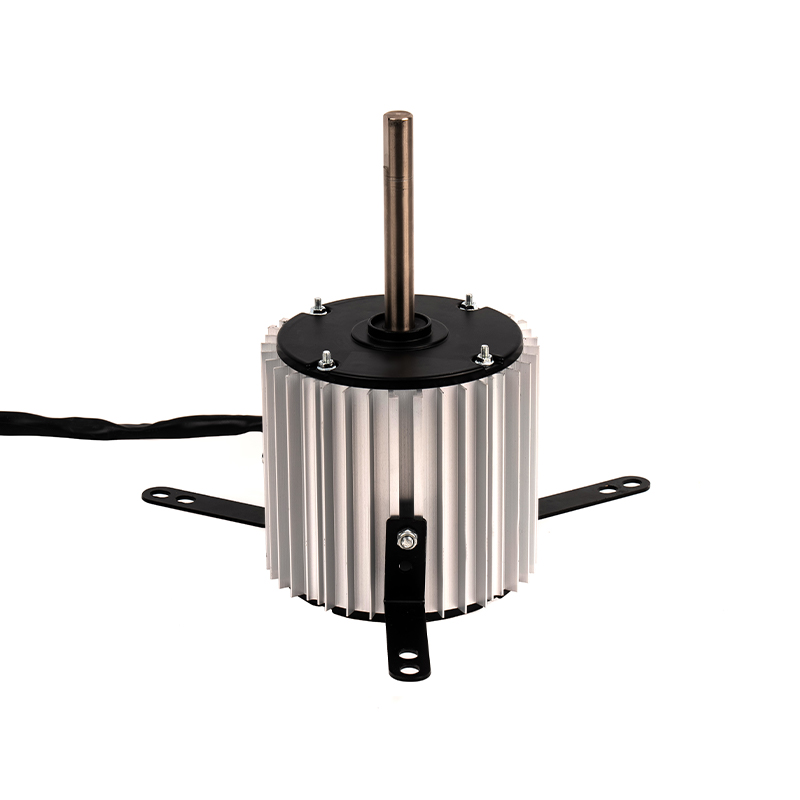
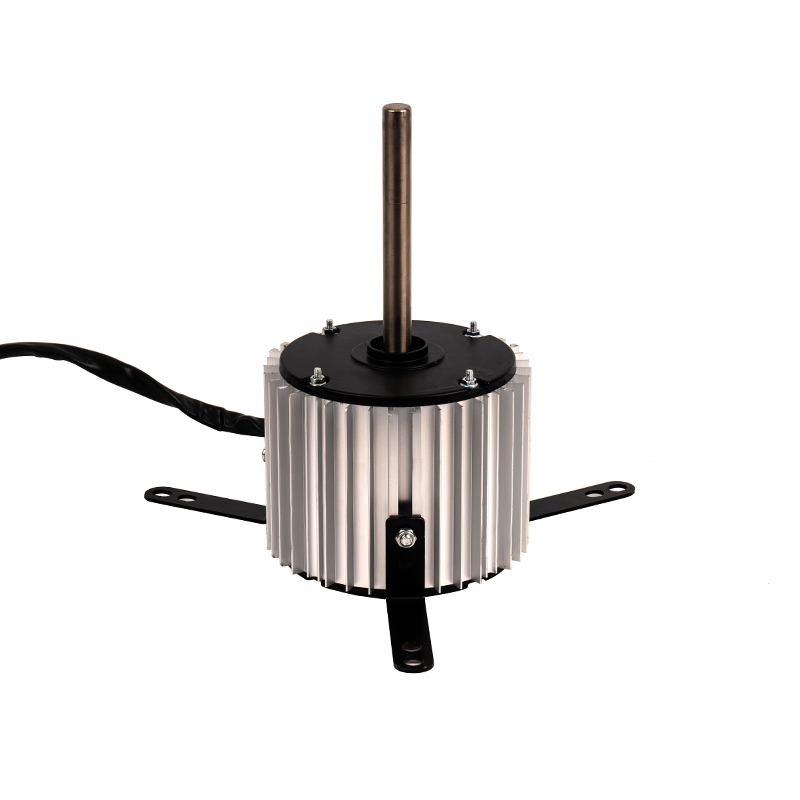
Energy Efficiency and Consistency
A Small Heating AC Motor is generally more energy-efficient than larger AC motors or DC motors, particularly when used in heating systems. AC motors are designed to operate efficiently at constant speeds, making them ideal for heating applications where the motor doesn't need to change speed frequently. This consistent operation leads to reliable and predictable energy consumption. Unlike DC motors, which may suffer from energy losses due to the need for more complex electronic controls to maintain speed, Small Heating AC Motors typically offer lower operational costs in the long run due to their inherent simplicity and efficiency in steady-state conditions.
Simple Design and Maintenance
One of the significant advantages of Small Heating AC Motors is their relatively simple design compared to DC motors. DC motors require additional components like commutators and brushes to regulate current flow, which can lead to higher maintenance costs and potential for wear over time. In contrast, Small Heating AC Motors are usually brushless, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and enhancing their reliability in heating applications. Additionally, the absence of brushes in AC motors eliminates the risk of issues like arcing and brush wear, making them more suitable for long-term use in environments where consistent performance is required.
Compact Size and Cost-Effectiveness
Small Heating AC Motors are typically smaller and more compact than their larger AC counterparts, allowing them to fit easily into space-constrained heating systems such as portable heaters or small HVAC units. This compactness also often translates to lower initial costs compared to larger AC motors, which are usually designed for more industrial-scale heating systems and require higher voltage and infrastructure. As a result, Small Heating AC Motors are ideal for use in consumer-facing heating products where space, cost, and ease of installation are critical factors.
Robustness and Durability
In heating applications, Small Heating AC Motors tend to be more robust and durable than DC motors due to their simple construction. The lack of brushes and commutators reduces the chances of component failure and the buildup of heat in critical areas. Furthermore, AC motors are often designed for continuous operation, which is particularly important in heating systems that need to run for extended periods without failure. This durability makes them more reliable in demanding heating environments, such as fan-driven heaters, space heaters, or small electric furnaces.
Better Heat Dissipation and Efficiency in High-Temperature Environments
Small Heating AC Motors are often specifically designed to handle high temperatures, which are common in heating applications. Their design incorporates better heat dissipation mechanisms, which allows them to perform efficiently even in environments where high thermal loads are present. Unlike larger AC motors, which may require additional cooling systems to operate in high-heat conditions, Small Heating AC Motors typically come with integrated cooling features that are optimized for steady operation without overheating. This makes them particularly well-suited for long-duration heating applications where the motor is continuously exposed to heat.
Steady Power Supply and Low-Voltage Operation
Another advantage of Small Heating AC Motors is their ability to work effectively with standard AC power supplies (such as 110V or 220V systems). This makes them ideal for residential or commercial heating systems, as they are compatible with readily available power grids without the need for specialized equipment or converters, unlike some DC motors that may require more complex power systems. The motor’s ability to work directly with low-voltage AC sources also contributes to energy efficiency and simpler integration into standard systems, making them more convenient and cost-effective for heating applications.
Reliability and Reduced Risk of Overload
AC motors, including Small Heating AC Motors, are generally less prone to overloading than DC motors, especially in steady-state heating applications. The fixed-speed nature of AC motors in heating systems ensures that the motor is always operating within a defined set of parameters, minimizing the risk of overcurrent conditions or overheating. In contrast, DC motors may require more sophisticated control systems to manage speed and torque, which can sometimes lead to failures or inefficiencies if the system is not properly tuned.


 English
English عربى
عربى ++86 13524608688
++86 13524608688












