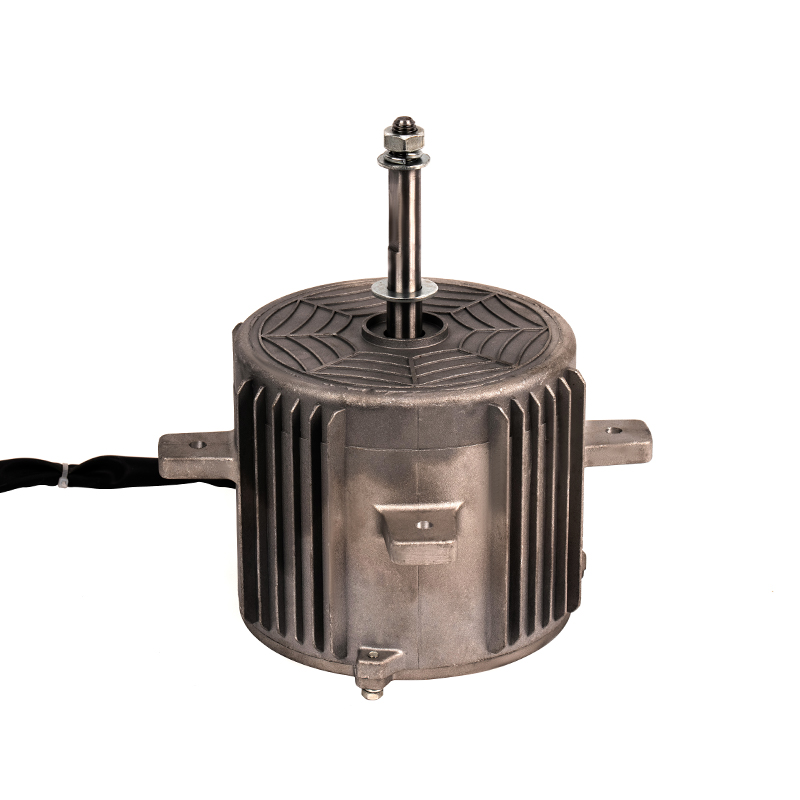
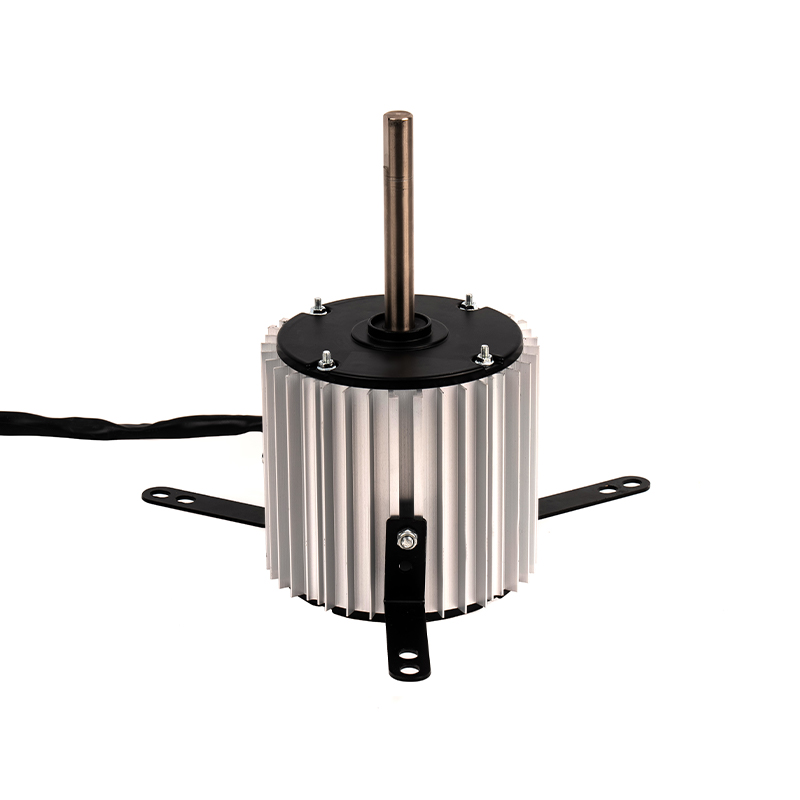
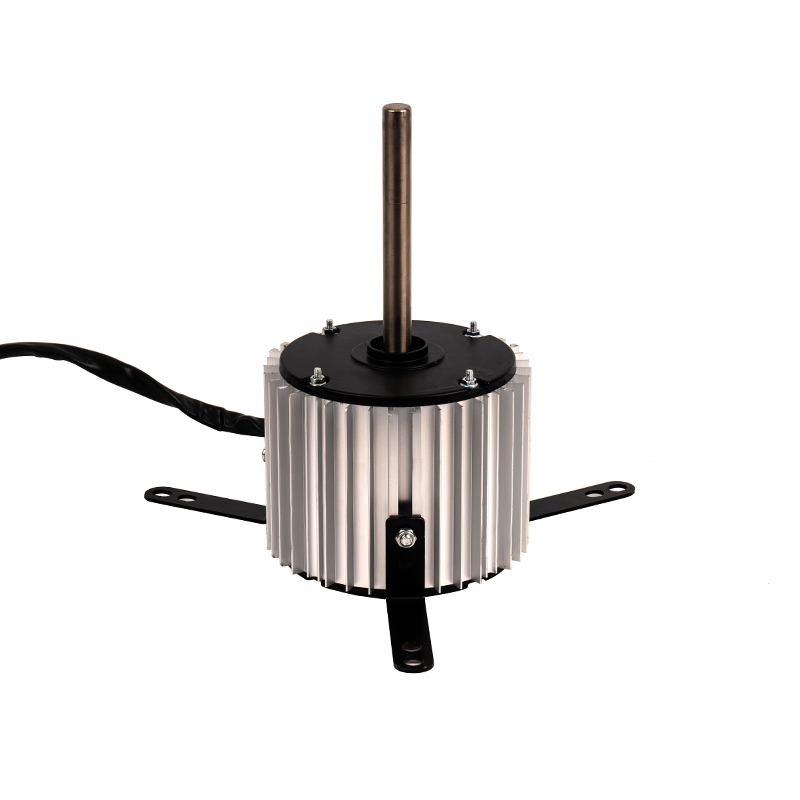
Air Circulation and Distribution
The Heating AC Motor serves as the driving force behind the air circulation process in forced air heating systems. By powering the blower fan or air handler, the motor facilitates the movement of air through the ductwork, ensuring that the heated air from the furnace or heat pump is distributed evenly throughout the building. This movement of air is crucial for uniform heating in residential, commercial, and industrial environments. Without the Heating AC Motor, the distribution of heat would be inefficient, with heated air unable to reach all areas of the space, leading to cold spots and temperature fluctuations.
In forced air systems, the blower fan pushes air across a heat exchanger or heating element. The AC motor ensures that air passes over these components at the right speed and volume, allowing the system to regulate temperature efficiently. Similarly, in heat pump systems, the Heating AC Motor works in tandem with other components, like the compressor, to circulate air after it has been either heated or cooled, depending on the mode of operation.
Professional Consideration: The efficiency of the air circulation system is directly tied to the motor's performance. A high-quality motor ensures better temperature regulation, while a poorly performing motor may result in inefficient heating and higher energy consumption.
Enabling Efficient Heat Transfer
Efficient heat transfer is a key aspect of both forced air heating and heat pump systems. In heat pumps, the Heating AC Motor plays a pivotal role in driving the compressor and the evaporator coil system, which are essential for heat exchange. The compressor, which is powered by the motor, circulates refrigerant throughout the system. As refrigerant absorbs heat from the air outside (in heating mode) or releases heat indoors (in cooling mode), the motor ensures that the entire process runs smoothly and without interruption.
For forced air heaters, the motor helps circulate air over the heat exchanger or heating elements, allowing the air to absorb heat efficiently. This heated air is then transported through the ducts to achieve the desired indoor temperature. Without the motor ensuring the right airflow, the system would struggle to transfer heat effectively, leading to poor energy efficiency and an inconsistent temperature throughout the space.
Professional Consideration: The motor’s efficiency and speed control mechanisms can enhance the heat transfer process, improving system performance by reducing energy losses and ensuring maximum heat absorption by the air.
Temperature Control and Consistency
In heating systems, temperature consistency is critical for user comfort, and the Heating AC Motor plays a central role in achieving this. In forced air heating systems, the motor operates the fan to move air at a controlled speed. If air movement is uneven or insufficient, temperature fluctuations may occur, leading to hot spots and cold spots in different rooms. By maintaining steady airflow, the motor helps distribute heat uniformly, providing consistent temperatures across the space.
In heat pump systems, the motor helps modulate the speed of the compressor and fan to maintain precise temperature control. This is particularly important during fluctuating outdoor temperatures or in variable climate zones. When the motor operates efficiently, it ensures that the heating (or cooling) system responds quickly to temperature adjustments, maintaining a comfortable and stable environment.
Dehumidification and Comfort
In heat pump systems, the Heating AC Motor plays a critical role in dehumidification as part of the cooling cycle. During the cooling process, the motor ensures air circulates over the evaporator coils, where moisture from the air condenses and is removed. The dehumidification process is particularly important in humid climates, as it helps maintain comfortable indoor air quality while keeping the temperature at a comfortable level.
In heating systems, particularly during colder months, the motor helps regulate airflow through the system, ensuring that warm air is evenly distributed. Without proper airflow management, air can become too dry, leading to discomfort such as dry skin, static electricity, or dry nasal passages. The Heating AC Motor’s role in maintaining an appropriate balance between temperature and humidity directly influences the overall comfort of the environment.
Energy Efficiency and Control
The Heating AC Motor is central to the energy efficiency of heating systems, particularly in modern, high-efficiency models. Older motors often operated at a constant speed, resulting in wasted energy when the system did not require maximum air circulation. However, variable speed motors now offer more precise control over airflow, adjusting fan speed based on the demand for heat. This ability to adapt to changing conditions significantly reduces energy consumption while still maintaining consistent temperature control.
In heat pump systems, the motor operates in conjunction with advanced thermostats or smart controls, adjusting the compressor and fan speed to optimize efficiency. For example, when the system is not running at full capacity, the motor reduces its speed to conserve energy, only ramping up when additional heat or cooling is required. This dynamic control ensures that energy is used only when necessary, reducing waste.


 English
English عربى
عربى ++86 13524608688
++86 13524608688












