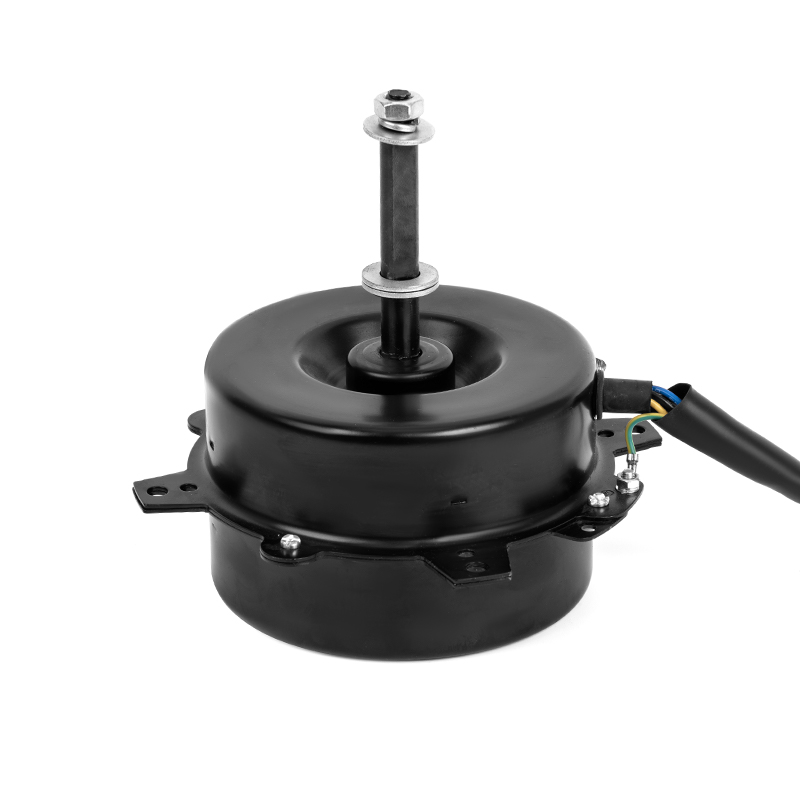
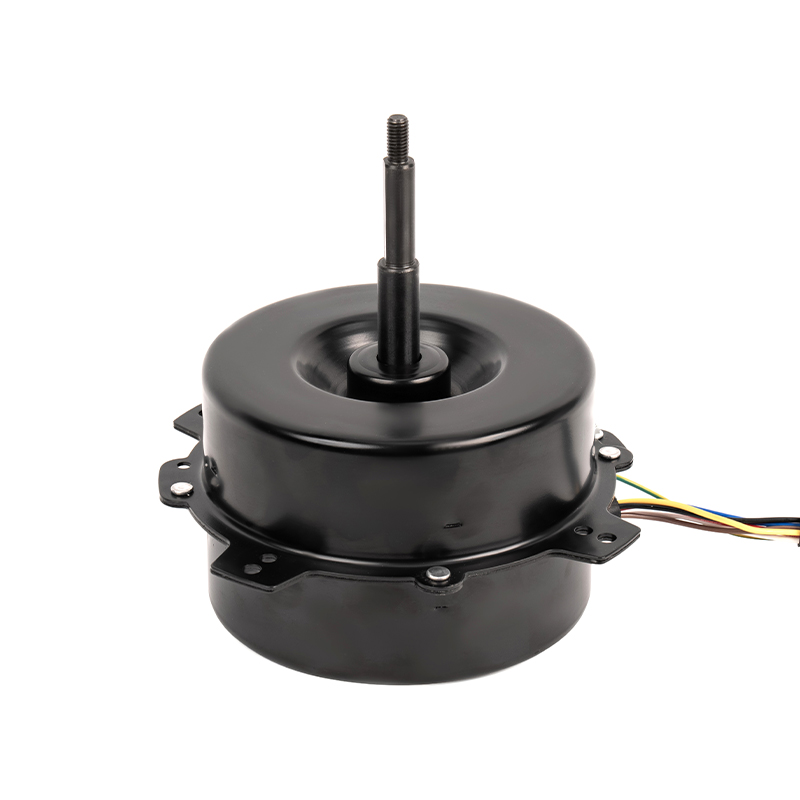
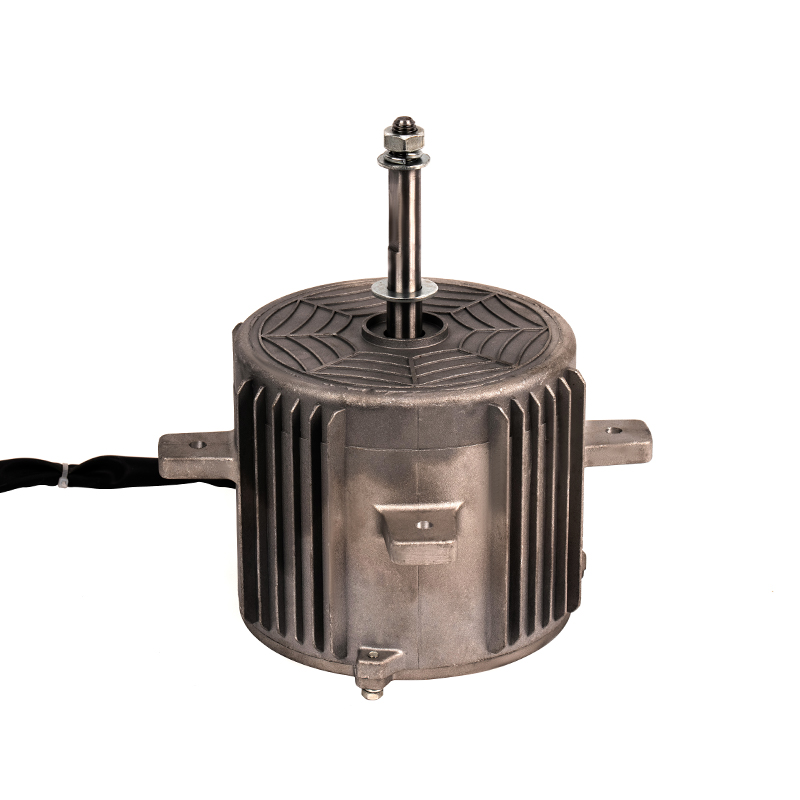
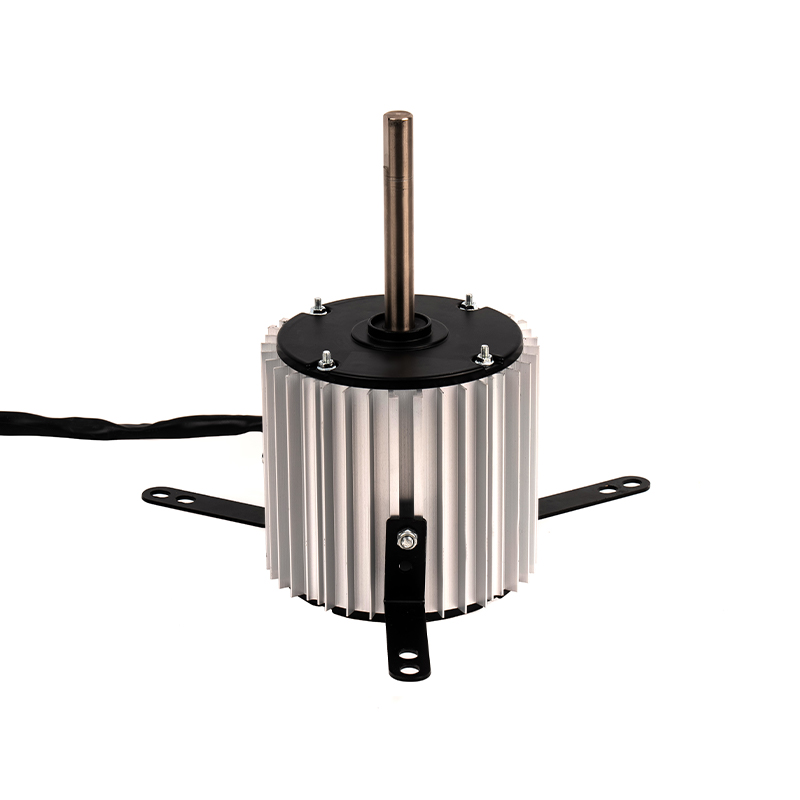
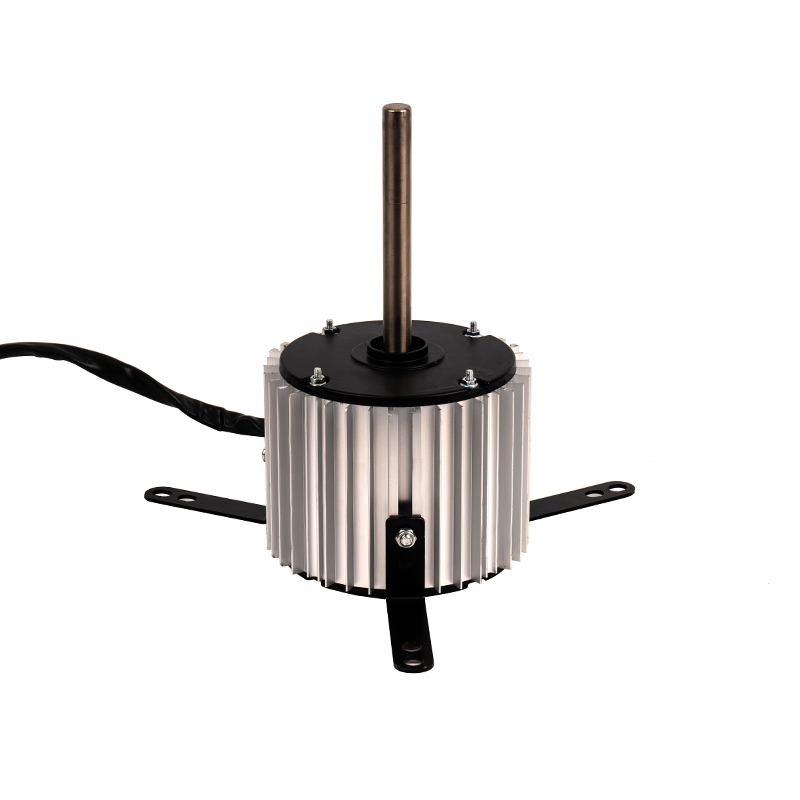
The Range Hood DC Motor offers advanced variable speed control, enabling the motor to adjust its rotational speed according to the intensity of cooking activities. Traditional AC motors, in contrast, often operate at a fixed speed, meaning they run at full capacity even when less suction power is needed, such as when cooking light meals or during idle periods. DC motors are designed to be more responsive to changes in airflow demand, dynamically adjusting their speed to match the level of cooking-related air contaminants like smoke or grease. This capability ensures that the range hood consumes only the power necessary for the current situation, resulting in lower overall energy consumption during lighter use. By operating at reduced speeds when possible, the motor minimizes unnecessary energy expenditure and enhances overall energy efficiency.
One of the distinct advantages of the Range Hood DC Motor is its efficiency at lower speeds. DC motors are optimized to operate efficiently even when running at slower speeds, which is the most common scenario in many household kitchens. When cooking light meals or simply needing general air circulation, a DC motor can maintain optimal suction power while using significantly less energy compared to a traditional AC motor, which tends to consume more power at all speeds. In practical terms, this means that a DC motor can provide sufficient airflow to remove smoke, grease, and odors during everyday use without wasting energy by running at higher speeds unnecessarily. This leads to significant energy savings over time, especially in kitchens where the range hood is used frequently but not always at full power.
Traditional AC motors are less energy-efficient than DC motors due to inherent power losses during operation. AC motors require more electrical energy to generate mechanical motion, and a significant portion of that energy is lost as heat, primarily due to the alternating current's electromagnetic fields. In contrast, DC motors are more efficient in converting electrical energy into mechanical motion, with fewer energy losses during the process. The energy that is used by a DC motor is more effectively transferred into air movement, reducing waste in the system. The result is a more efficient range hood that consumes less energy to achieve the same or better performance levels, contributing to reduced power consumption and overall lower operating costs.
Many modern Range Hood DC Motors feature intelligent motor control technology, which allows the motor to respond to real-time conditions in the kitchen. Sensors monitor factors such as the presence of smoke, steam, temperature fluctuations, and air quality. Based on this data, the motor can adjust its speed accordingly to optimize airflow and suction power. For example, when there is a sudden surge of smoke or steam, the motor can automatically ramp up to its maximum speed to clear the air quickly. Conversely, if the air quality improves or cooking activity decreases, the motor will reduce its speed, using less power. This intelligent response system ensures that the motor operates in the most energy-efficient manner, reducing unnecessary energy consumption and improving the overall efficiency of the range hood system.
DC motors produce less heat compared to their AC counterparts. AC motors, particularly those running at higher speeds, can generate significant heat due to inefficiencies in their operation, such as energy losses in the motor windings. This not only impacts energy efficiency but can also lead to reduced motor performance over time, as overheating can cause wear and tear on the motor components. In contrast, DC motors operate at a lower temperature because they are more efficient at converting electrical energy into mechanical work, producing less heat in the process. The reduced heat generation in DC motors not only contributes to a more energy-efficient system but also improves the longevity of the motor and other components in the range hood.


 English
English عربى
عربى ++86 13524608688
++86 13524608688












